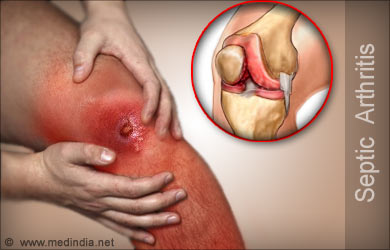
What are the Causes of Septic Arthritis?Bacteria are the commonest organisms that cause septic arthritis. The bacteria that are commonly implicated in this condition include Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, Hemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhea, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The organisms reach the joint space through blood from the source of infection, which could be an abscess or an injured tissue. They could also spread locally from an infection in the nearby tissues. Viruses, mycobacteria and fungi can also cause septic arthritis.

What are the Risk Factors of Septic Arthritis?Patients with reduced immunity are at a risk of suffering from septic arthritis. These include:
 Patients suffering from HIV, diabetes and rheumatic disease.
Patients suffering from HIV, diabetes and rheumatic disease.

 Patients on medications that reduce immunity like steroids, anticancer drugs, azathioprine and cyclosporine.
Patients on medications that reduce immunity like steroids, anticancer drugs, azathioprine and cyclosporine. Young children and elderly people.
Young children and elderly people.
Other predisposing factors for septic arthritis are:
 Injury to a joint or a neighboring area.
Injury to a joint or a neighboring area.
 Presence of prosthetic joints.
Presence of prosthetic joints.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Septic Arthritis?
The patient presents with the following features:
 Fever with chills
Fever with chills
 Pain and swelling over the affected joint
Pain and swelling over the affected joint
 On examination, the joint appears warm, red, swollen and stiff. The patient is unable to move the limb at the affected joint.
On examination, the joint appears warm, red, swollen and stiff. The patient is unable to move the limb at the affected joint.How can we Diagnose Septic Arthritis?
Septic arthritis is diagnosed using the following tests:
 Joint fluid examination: The joint fluid is obtained from the affected joint using a needle and syringe. It is examined under the microscope for the presence of white blood cells, which suggest infection. Culture of the fluid will identify the organism responsible for the infection and help to determine its sensitivity to the antimicrobial drug.
Joint fluid examination: The joint fluid is obtained from the affected joint using a needle and syringe. It is examined under the microscope for the presence of white blood cells, which suggest infection. Culture of the fluid will identify the organism responsible for the infection and help to determine its sensitivity to the antimicrobial drug.
 X-ray: X-ray of the joint can reveal evidence of bone injury.
X-ray: X-ray of the joint can reveal evidence of bone injury.
 MRI: MRI can aid in the assessment of joint destruction.
MRI: MRI can aid in the assessment of joint destruction.

How can Septic Arthritis be Treated?Treatment of septic arthritis includes the following:
 Antibiotics or other antimicrobials are used in the treatment of septic arthritis. Treatment is started immediately, using broad-spectrum antimicrobials initially. This type of medication covers a wide range of pathogens. Later, based on culture report, a drug that acts specifically against the causative organism will be given. Treatment is given intravenously for a duration of four to six weeks.
Antibiotics or other antimicrobials are used in the treatment of septic arthritis. Treatment is started immediately, using broad-spectrum antimicrobials initially. This type of medication covers a wide range of pathogens. Later, based on culture report, a drug that acts specifically against the causative organism will be given. Treatment is given intravenously for a duration of four to six weeks.

 For rapid recovery, the joint fluid is drained.
For rapid recovery, the joint fluid is drained. The joint can be irrigated and infected tissue removed by arthroscopy. Open surgery may be necessary in some cases.
The joint can be irrigated and infected tissue removed by arthroscopy. Open surgery may be necessary in some cases.
No comments:
Post a Comment